Fed Chairman Jerome Powell held a press conference at the annual Jackson Hole economic conference today, and he all but said that a September cut to the federal funds rate is a done deal: “The time has come for policy to adjust. The direction of travel is clear.”
Naturally he threw in the usual propaganda phrases about how the Fed is data driven. He continues: “the timing and pace of rate cuts will depend on incoming data, the evolving outlook, and the balance of risks.”
Remember, with its official statements, the Fed is always careful to try and give the impression that it is not a political organization and responds only to economic data.
But, for whatever reason, Powell and the Fed have now decided official CPI inflation is low enough for the central bank get away with NEW infusions of easy money, even as stocks, rents, home prices, and food prices are all at record high.
On price inflation, Powell all but declares “mission accomplished”: “With an appropriate dialing back of policy restraint, there is good reason to think that the economy will get back to two percent inflation while maintaining a strong labor market.”
So, in addition declaring victory over rising prices – even though last month’s official CPI growth was still nearly 3 percent— Powell is again pushing the myth of the “soft landing” even though there is absolutely no reason to believe the Fed can engineer such a thing.
In fact, if anything, the fact that the Fed now plans to start cutting rates is one of the strongest recession signals we can get.
If we look back at the relationship between rate cuts and recessions, we see that in almost every case that recessions begin shortly after the Fed starts a cycle of rate cuts. The fed started cutting the Fed funds rate in 1989. Then we got the recession of the early 90s. In late 2000, the fed started the rate cuts again. We got a recession in 2001. The Fed did it again in late 2007. The recession began in December 2007, followed by a financial crisis several months later. This relationship even holds for the 2020 recession because even without covid there would have been a recession in late 2020. The Fed had begun to ease the target rate in summer 2019.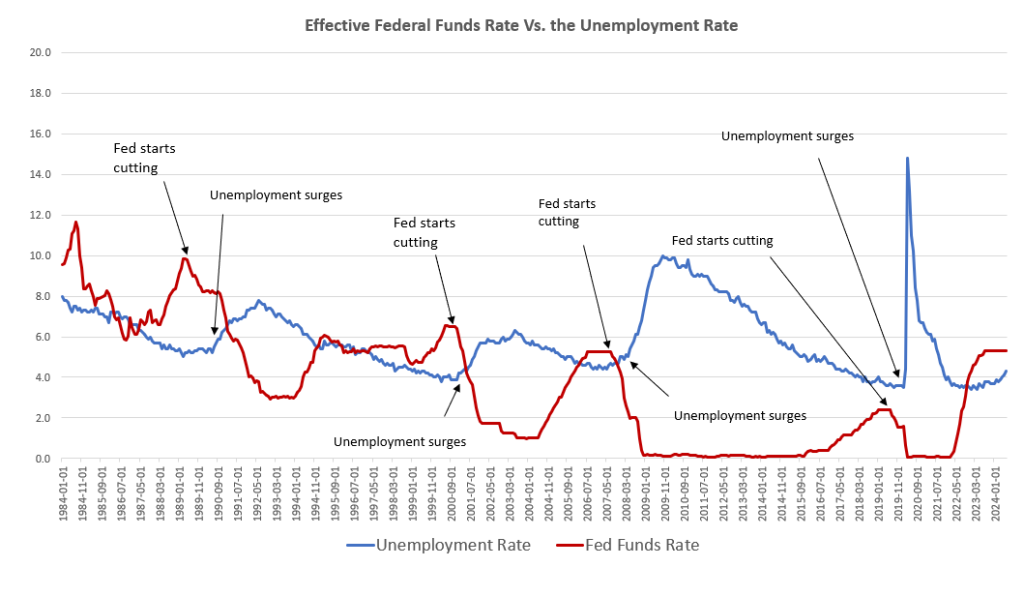
Fed rate cuts don’t cause recessions, of course. The boom-bust cycle is caused by reckless Fed-driven money creation.
But it makes sense that the Fed hits the panic button and starts cutting rates when it does because the Fed is reacting to fears about impending recessions. The same is true this time around. The Fed has no special prediction skills, so it sees what the rest of us see: a weakening economy and a much less rosy employment picture than what was sold to us by the administration over the past year. July’s weak jobs report with rising unemployment, combined with this week’s massive downward revision in 2023-2024 jobs numbers, gives us good reason to figure that the Fed is now trying to prevent a recession by flooding the economy with more easy money. […]
— Read More: mises.org
Five Things New “Preppers” Forget When Getting Ready for Bad Times Ahead
The preparedness community is growing faster than it has in decades. Even during peak times such as Y2K, the economic downturn of 2008, and Covid, the vast majority of Americans made sure they had plenty of toilet paper but didn’t really stockpile anything else.
Things have changed. There’s a growing anxiety in this presidential election year that has prompted more Americans to get prepared for crazy events in the future. Some of it is being driven by fearmongers, but there are valid concerns with the economy, food supply, pharmaceuticals, the energy grid, and mass rioting that have pushed average Americans into “prepper” mode.
There are degrees of preparedness. One does not have to be a full-blown “doomsday prepper” living off-grid in a secure Montana bunker in order to be ahead of the curve. In many ways, preparedness isn’t about being able to perfectly handle every conceivable situation. It’s about being less dependent on government for as long as possible. Those who have proper “preps” will not be waiting for FEMA to distribute emergency supplies to the desperate masses.
Below are five things people new to preparedness (and sometimes even those with experience) often forget as they get ready. All five are common sense notions that do not rely on doomsday in order to be useful. It may be nice to own a tank during the apocalypse but there’s not much you can do with it until things get really crazy. The recommendations below can have places in the lives of average Americans whether doomsday comes or not.
Note: The information provided by this publication or any related communications is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as financial advice. We do not provide personalized investment, financial, or legal advice.
Secured Wealth
Whether in the bank or held in a retirement account, most Americans feel that their life’s savings is relatively secure. At least they did until the last couple of years when de-banking, geopolitical turmoil, and the threat of Central Bank Digital Currencies reared their ugly heads.
It behooves Americans to diversify their holdings. If there’s a triggering event or series of events that cripple the financial systems or devalue the U.S. Dollar, wealth can evaporate quickly. To hedge against potential turmoil, many Americans are looking in two directions: Crypto and physical precious metals.
There are huge advantages to cryptocurrencies, but there are also inherent risks because “virtual” money can become challenging to spend. Add in the push by central banks and governments to regulate or even replace cryptocurrencies with their own versions they control and the risks amplify. There’s nothing wrong with cryptocurrencies today but things can change rapidly.
As for physical precious metals, many Americans pay cash to keep plenty on hand in their safe. Rolling over or transferring retirement accounts into self-directed IRAs is also a popular option, but there are caveats. It can often take weeks or even months to get the gold and silver shipped if the owner chooses to close their account. This is why Genesis Gold Group stands out. Their relationship with the depositories allows for rapid closure and shipping, often in less than 10 days from the time the account holder makes their move. This can come in handy if things appear to be heading south.
Lots of Potable Water
One of the biggest shocks that hit new preppers is understanding how much potable water they need in order to survive. Experts claim one gallon of water per person per day is necessary. Even the most conservative estimates put it at over half-a-gallon. That means that for a family of four, they’ll need around 120 gallons of water to survive for a month if the taps turn off and the stores empty out.
Being near a fresh water source, whether it’s a river, lake, or well, is a best practice among experienced preppers. It’s necessary to have a water filter as well, even if the taps are still working. Many refuse to drink tap water even when there is no emergency. Berkey was our previous favorite but they’re under attack from regulators so the Alexapure systems are solid replacements.
For those in the city or away from fresh water sources, storage is the best option. This can be challenging because proper water storage containers take up a lot of room and are difficult to move if the need arises. For “bug in” situations, having a larger container that stores hundreds or even thousands of gallons is better than stacking 1-5 gallon containers. Unfortunately, they won’t be easily transportable and they can cost a lot to install.
Water is critical. If chaos erupts and water infrastructure is compromised, having a large backup supply can be lifesaving.
Pharmaceuticals and Medical Supplies
There are multiple threats specific to the medical supply chain. With Chinese and Indian imports accounting for over 90% of pharmaceutical ingredients in the United States, deteriorating relations could make it impossible to get the medicines and antibiotics many of us need.
Stocking up many prescription medications can be hard. Doctors generally do not like to prescribe large batches of drugs even if they are shelf-stable for extended periods of time. It is a best practice to ask your doctor if they can prescribe a larger amount. Today, some are sympathetic to concerns about pharmacies running out or becoming inaccessible. Tell them your concerns. It’s worth a shot. The worst they can do is say no.
If your doctor is unwilling to help you stock up on medicines, then Jase Medical is a good alternative. Through telehealth, they can prescribe daily meds or antibiotics that are shipped to your door. As proponents of medical freedom, they empathize with those who want to have enough medical supplies on hand in case things go wrong.
Energy Sources
The vast majority of Americans are locked into the grid. This has proven to be a massive liability when the grid goes down. Unfortunately, there are no inexpensive remedies.
Those living off-grid had to either spend a lot of money or effort (or both) to get their alternative energy sources like solar set up. For those who do not want to go so far, it’s still a best practice to have backup power sources. Diesel generators and portable solar panels are the two most popular, and while they’re not inexpensive they are not out of reach of most Americans who are concerned about being without power for extended periods of time.
Natural gas is another necessity for many, but that’s far more challenging to replace. Having alternatives for heating and cooking that can be powered if gas and electric grids go down is important. Have a backup for items that require power such as manual can openers. If you’re stuck eating canned foods for a while and all you have is an electric opener, you’ll have problems.
Don’t Forget the Protein
When most think about “prepping,” they think about their food supply. More Americans are turning to gardening and homesteading as ways to produce their own food. Others are working with local farmers and ranchers to purchase directly from the sources. This is a good idea whether doomsday comes or not, but it’s particularly important if the food supply chain is broken.
Most grocery stores have about one to two weeks worth of food, as do most American households. Grocers rely heavily on truckers to receive their ongoing shipments. In a crisis, the current process can fail. It behooves Americans for multiple reasons to localize their food purchases as much as possible.
Long-term storage is another popular option. Canned foods, MREs, and freeze dried meals are selling out quickly even as prices rise. But one component that is conspicuously absent in shelf-stable food is high-quality protein. Most survival food companies offer low quality “protein buckets” or cans of meat, but they are often barely edible.
Prepper All-Naturals offers premium cuts of steak that have been cooked sous vide and freeze dried to give them a 25-year shelf life. They offer Ribeye, NY Strip, and Tenderloin among others.
Having buckets of beans and rice is a good start, but keeping a solid supply of high-quality protein isn’t just healthier. It can help a family maintain normalcy through crises.
Prepare Without Fear
With all the challenges we face as Americans today, it can be emotionally draining. Citizens are scared and there’s nothing irrational about their concerns. Being prepared and making lifestyle changes to secure necessities can go a long way toward overcoming the fears that plague us. We should hope and pray for the best but prepare for the worst. And if the worst does come, then knowing we did what we could to be ready for it will help us face those challenges with confidence.






Interesting phenomena. You’d think more money in circulation would result in more job-producing activity. I’m no economist, but I guess it might make some sense to me considering most of the money being loaned is private money, even when the government is printing money. So interest rates set by the Fed ripple through. Investors then earn less return, which may slow investment, change strategies, etc. That, and whatever the money is being borrowed for is not going to any sort of job-producing activity. I imagine it is difficult to quantify how much is actually in circulation in a manner that amounts to economic activity, and how much is held back. And I’m sure there are other factors I don’t know and haven’t thought of.
The theoretical egg heads aren’t likely to do anything unless they fully understand the “why”. But if you have an isolated and measurable cause and effect, you don’t have to understand why. Right, science doesn’t know exactly what gravity is. But it’s behavior is consistent enough, measurable enough, observable enough, that it is used and taken into account all day every day.
That’s the difference between a theoretical scientist and a practical engineer.
We have too many egg-headed theorists, with their heads in the clouds. And not enough “engineers” dealing with the practical reality.
Interesting to think about, though.
* its